Rohner, E., Yang, R., Foo, Ok. S., Goedel, A. & Chien, Ok. R. Unlocking the promise of mRNA therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 40, 1586–1600 (2022).
Huang, X. et al. The panorama of mRNA nanomedicine. Nat. Med. 28, 2273–2287 (2022).
Jackson, L. A. et al. An mRNA vaccine towards SARS-CoV-2—preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1920–1931 (2020).
Liu, C. et al. mRNA-based most cancers therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Most cancers 23, 526–543 (2023).
Barbier, A. J., Jiang, A. Y., Zhang, P., Wooster, R. & Anderson, D. G. The medical progress of mRNA vaccines and immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 40, 840–854 (2022).
Frankiw, L., Baltimore, D. & Li, G. Various mRNA splicing in most cancers immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19, 675–687 (2019).
Lorentzen, C. L., Haanen, J. B., Met, Ö & Svane, I. M. Medical advances and ongoing trials of mRNA vaccines for most cancers therapy. Lancet Oncol. 23, e450–e458 (2022).
Dolgin, E. Personalised most cancers vaccines go first main medical take a look at. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 22, 607–609 (2023).
Blagden, S. P. & Willis, A. E. The organic and therapeutic relevance of mRNA translation in most cancers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 8, 280–291 (2011).
Vitale, I., Shema, E., Loi, S. & Galluzzi, L. Intratumoral heterogeneity in most cancers development and response to immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 27, 212–224 (2021).
Martin, J. D., Cabral, H., Stylianopoulos, T. & Jain, R. Ok. Bettering most cancers immunotherapy utilizing nanomedicines: progress, alternatives and challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 17, 251–266 (2020).
Junttila, M. R. & de Sauvage, F. J. Affect of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature 501, 346–354 (2013).
Johnson, D. B., Nebhan, C. A., Moslehi, J. J. & Balko, J. M. Immune-checkpoint inhibitors: long-term implications of toxicity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 19, 254–267 (2022).
Hotz, C. et al. Native supply of mRNA-encoded cytokines promotes antitumor immunity and tumor eradication throughout a number of preclinical tumor fashions. Sci. Transl. Med. 13, eabc7804 (2021).
Hausser, J. & Alon, U. Tumour heterogeneity and the evolutionary trade-offs of most cancers. Nat. Rev. Most cancers 20, 247–257 (2020).
Krysko, D. V. et al. Immunogenic cell loss of life and DAMPs in most cancers remedy. Nat. Rev. Most cancers 12, 860–875 (2012).
Galluzzi, L., Buqué, A., Kepp, O., Zitvogel, L. & Kroemer, G. Immunogenic cell loss of life in most cancers and infectious illness. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 17, 97–111 (2017).
Meier, P., Legrand, A. J., Adam, D. & Silke, J. Immunogenic cell loss of life in most cancers: concentrating on necroptosis to induce antitumour immunity. Nat. Rev. Most cancers 24, 299–315 (2024).
Galon, J. & Bruni, D. Approaches to deal with immune sizzling, altered and chilly tumours with mixture immunotherapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 18, 197–218 (2019).
Li, F. et al. mRNA lipid nanoparticle-mediated pyroptosis sensitizes immunologically chilly tumors to checkpoint immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 14, 4223 (2023).
Li, Y. et al. Multifunctional oncolytic nanoparticles ship self-replicating IL-12 RNA to remove established tumors and prime systemic immunity. Nat. Most cancers 1, 882–893 (2020).
Zhang, D. et al. Enhancing CRISPR/Cas gene enhancing by means of modulating mobile mechanical properties for most cancers remedy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 777–787 (2022).
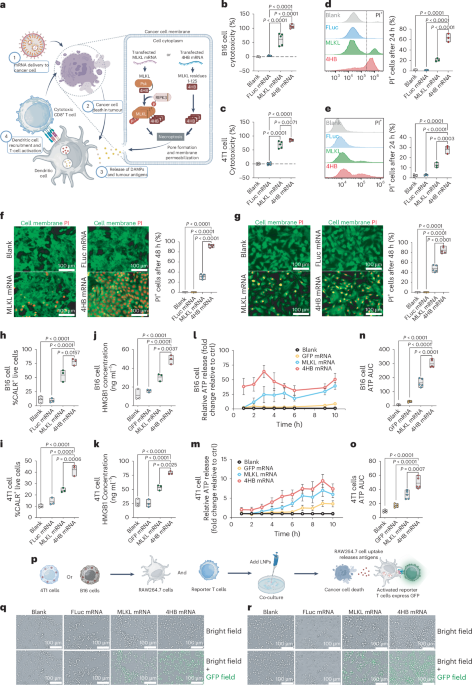
Van Hoecke, L. et al. Therapy with mRNA coding for the necroptosis mediator MLKL induces antitumor immunity directed towards neo-epitopes. Nat. Commun. 9, 3417 (2018).
Kon, E., Advert-El, N., Hazan-Halevy, I., Stotsky-Oterin, L. & Peer, D. Concentrating on most cancers with mRNA–lipid nanoparticles: key issues and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 20, 739–754 (2023).
Gaur, A. et al. Characterization of microRNA expression ranges and their organic correlates in human most cancers cell traces. Most cancers Res. 67, 2456–2468 (2007).
Volinia, S. et al. A microRNA expression signature of human stable tumors defines most cancers gene targets. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 2257–2261 (2006).
Dhawan, A., Scott, J. G., Harris, A. L. & Buffa, F. M. Pan-cancer characterisation of microRNA throughout most cancers hallmarks reveals microRNA-mediated downregulation of tumour suppressors. Nat. Commun. 9, 5228 (2018).
Feikin, D. R. et al. Length of effectiveness of vaccines towards SARS-CoV-2 an infection and COVID-19 illness: outcomes of a scientific evaluation and meta-regression. Lancet 399, 924–944 (2022).
Vandenabeele, P., Bultynck, G. & Savvides, S. N. Pore-forming proteins as drivers of membrane permeabilization in cell loss of life pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 312–333 (2023).
Pasparakis, M. & Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis and its function in irritation. Nature 517, 311–320 (2015).
Hildebrand, J. M. et al. Activation of the pseudokinase MLKL unleashes the four-helix bundle area to induce membrane localization and necroptotic cell loss of life. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 15072–15077 (2014).
Faramin Lashkarian, M. et al. MicroRNA-122 in human cancers: from mechanistic to medical views. Most cancers Cell Int 23, 29 (2023).
Hsu, S. H. et al. Important metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic features of miR-122 in liver. J. Clin. Make investments. 122, 2871–2883 (2012).
Galluzzi, L., Guilbaud, E., Schmidt, D., Kroemer, G. & Marincola, F. M. Concentrating on immunogenic cell stress and loss of life for most cancers remedy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 23, 445–460 (2024).
Mensurado, S., Blanco-Domínguez, R. & Silva-Santos, B. The rising roles of γδ T cells in most cancers immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 20, 178–191 (2023).
Mantovani, A., Allavena, P., Marchesi, F. & Garlanda, C. Macrophages as instruments and targets in most cancers remedy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 21, 799–820 (2022).
Oliveira, G. & Wu, C. J. Dynamics and specificities of T cells in most cancers immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Most cancers 23, 295–316 (2023).
Cho, Y. et al. Phosphorylation-driven meeting of the RIP1-RIP3 complicated regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced irritation. Cell 137, 1112–1123 (2009).
Najafov, A., Chen, H. & Yuan, J. Necroptosis and most cancers. Tendencies Most cancers 3, 294–301 (2017).
Kim, S. et al. Enchancment of therapeutic impact by way of inducing non-apoptotic cell loss of life utilizing mRNA-protection nanocage. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13, 2400240 (2024).
Dondelinger, Y. et al. MLKL compromises plasma membrane integrity by binding to phosphatidylinositol phosphates. Cell Rep. 7, 971–981 (2014).
Hänggi, Ok. et al. Interleukin-1α launch throughout necrotic-like cell loss of life generates myeloid-driven immunosuppression that restricts anti-tumor immunity. Most cancers Cell 42, 2015–2031.e2011 (2024).
Seifert, L. et al. The necrosome promotes pancreatic oncogenesis by way of CXCL1 and Mincle-induced immune suppression. Nature 532, 245–249 (2016).
Dagogo-Jack, I. & Shaw, A. T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to most cancers therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15, 81–94 (2018).
Li, B. et al. Combinatorial design of nanoparticles for pulmonary mRNA supply and genome enhancing. Nat. Biotechnol. 41, 1410–1415 (2023).
Chen, J. et al. Combinatorial design of ionizable lipid nanoparticles for muscle-selective mRNA supply with minimized off-target results. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2309472120 (2023).
Hewitt, S. L. et al. Sturdy anticancer immunity from intratumoral administration of IL-23, IL-36γ, and OX40L mRNAs. Sci. Transl. Med. 11, eaat9143 (2019).
Feng, Z. et al. An in vitro-transcribed round RNA targets the mitochondrial internal membrane cardiolipin to ablate EIF4G2+PTBP1+ pan-adenocarcinoma. Nat. Most cancers 5, 30–46 (2024).
Jain, R. et al. MicroRNAs allow mRNA therapeutics to selectively program most cancers cells to self-destruct. Nucleic Acid Ther. 28, 285–296 (2018).
Xiao, Y. & Shi, J. Lipids and the rising RNA medicines. Chem. Rev. 121, 12109–12111 (2021).
Eygeris, Y., Gupta, M., Kim, J. & Sahay, G. Chemistry of lipid nanoparticles for RNA supply. Acc. Chem. Res. 55, 2–12 (2021).
Zhang, Y., Solar, C., Wang, C., Jankovic, Ok. E. & Dong, Y. Lipids and lipid derivatives for RNA supply. Chem. Rev. 121, 12181–12277 (2021).
Miao, L. et al. Supply of mRNA vaccines with heterocyclic lipids will increase anti-tumor efficacy by STING-mediated immune cell activation. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1174–1185 (2019).
Khoury, M. Ok., Gupta, Ok., Franco, S. R. & Liu, B. Necroptosis within the pathophysiology of illness. Am. J. Pathol. 190, 272–285 (2020).
Xu, Y. et al. AGILE platform: a deep studying powered method to speed up LNP improvement for mRNA supply. Nat. Commun. 15, 6305 (2024).
Charni-Natan, M. & Goldstein, I. Protocol for major mouse hepatocyte isolation. STAR Protoc. 1, 100086 (2020).
Li, J., Yao, Q. & Liu, D. Hydrodynamic cell supply for simultaneous institution of tumor progress in mouse lung, liver and kidney. Most cancers Biol. Ther. 12, 737–741 (2011).