As synthetic intelligence continues its speedy evolution, two phrases dominate the dialog: generative AI and the rising idea of agentic AI. Whereas each signify important developments, they carry very totally different implications for companies, significantly with regards to knowledge safety and cybersecurity.
This text unpacks what every expertise means, how they differ, and what their rise alerts for the way forward for digital belief and safety.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to techniques designed to create new outputs-such as textual content, pictures, code, and even music-by figuring out and replicating patterns from massive datasets. Fashions like GPT or DALLE study linguistic or visible constructions after which generate new content material in response to consumer prompts. These techniques are broadly utilized in areas akin to content material creation, customer support chatbots, design prototyping, and coding help. Their power lies in effectivity, creativity, and scalability, permitting organizations to supply human-like outputs at unprecedented velocity. On the identical time, generative AI comes with challenges: it may well hallucinate data, reinforce present biases, elevate mental property considerations, and unfold misinformation. Finally, its worth lies in amplifying creativity and productiveness, however its dangers stay tied to the high quality and accuracy of the info it learns from.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI represents the subsequent step within the evolution of synthetic intelligence. In contrast to generative AI, which produces outputs in response to prompts, agentic AI is designed to plan, determine, and act with a level of autonomy. These techniques function inside outlined targets and may execute duties independently, decreasing the necessity for fixed human intervention. For instance, an AI gross sales agent won’t solely draft outreach emails but in addition decide which shoppers to contact, schedule follow-ups, and refine its technique based mostly on responses. Core options of agentic AI embrace autonomy in decision-making, goal-directed conduct, and the capability for reasoning and self-correction. In essence, agentic AI is much less about imitation and extra about delegation-taking on operational duties that have been as soon as firmly in human arms.
The Key Variations between Generative and Agentic AI
Whereas generative and agentic AI share the identical basis of machine studying, their scope and influence diverge in significant methods. Generative AI is primarily designed to create-whether which means drafting a report, producing code snippets, or producing digital art work. Its outputs are guided by prompts, which suggests it stays largely depending on human enter to provoke and direct its perform. In contrast, agentic AI shouldn’t be confined to creation alone; it extends into decision-making and execution. These techniques are goal-driven, able to planning and performing with a stage of autonomy that reduces the necessity for fixed human oversight.
This distinction additionally shifts the danger panorama. Generative AI’s challenges sometimes middle on misinformation, bias, or reputational hurt brought on by inaccurate or inappropriate outputs. Agentic AI, nonetheless, raises operational and compliance considerations due to its capacity to behave independently. Errors, unintended actions, or the mishandling of delicate knowledge can have rapid and tangible penalties for organizations. In brief, generative AI informs, whereas agentic AI intervenes-a distinction that carries important implications for each knowledge safety and cybersecurity.
Implications for Knowledge Safety
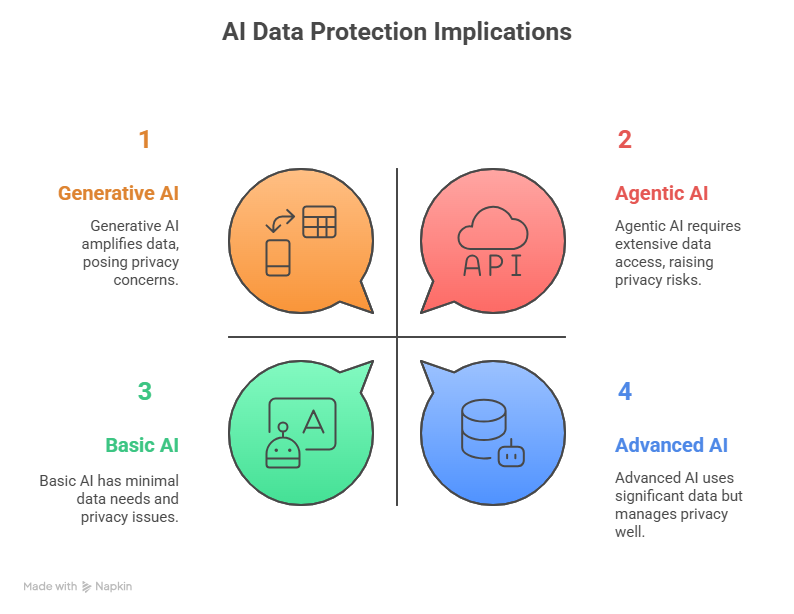
Each types of AI are solely as sturdy as the info they consume-but their influence on privateness and compliance differs.
- Knowledge Dependency:
Generative AI amplifies no matter it’s skilled on. Agentic AI requires real-time entry to enterprise and buyer knowledge, making accuracy and governance non-negotiable. - Privateness Challenges:
Autonomy could push agentic AI to entry delicate knowledge units (emails, monetary information, well being knowledge) with out specific human checks. This elevates dangers below frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. - Transparency and Belief:
To keep up belief, companies should construct auditability and explainability into AI operations-ensuring knowledge use may be traced and justified.
Cybersecurity Dangers and Alternatives
The rise of agentic AI introduces a paradox for cybersecurity leaders: it’s each a brand new menace vector and a protection mechanism.
- Threats:
- Malicious actors might exploit agentic AI to automate phishing, fraud, or denial-of-service assaults.
- Autonomous execution will increase the dimensions and velocity of potential cyberattacks.
- Alternatives:
- AI brokers can function always-on defenders, autonomously scanning for vulnerabilities, detecting anomalies, and neutralizing assaults in actual time.
- Generative AI can help analysts by drafting menace reviews or simulating assault patterns, whereas agentic AI can execute countermeasures.
- The Double-Edged Sword:
The identical autonomy that makes agentic AI highly effective additionally makes it harmful if compromised. A hijacked AI agent might trigger harm far sooner than a human adversary alone.
What’s Subsequent for Cybersecurity within the Age of Agentic AI?
The subsequent wave of cybersecurity shall be formed by how organizations select to control AI autonomy. Three priorities stand out as essential for balancing innovation with security.
1. Stronger Governance Frameworks
Clear accountability for AI actions is important. Organizations should outline who’s chargeable for outcomes, whereas additionally establishing protocols that guarantee human oversight stays a part of the method.
2. AI-on-AI Protection Methods
As adversaries more and more weaponize AI, defensive AI brokers shall be wanted to detect, counter, and neutralize threats in actual time. Constructing resilience into techniques requires assuming that attackers may also use autonomous instruments.
3. Human-in-the-Loop Fashions
Regardless of advances in autonomy, human judgment can’t be faraway from high-stakes selections. Retaining human authority in areas akin to privateness, finance, and security ensures that AI actions stay aligned with moral and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Generative AI modified the way in which companies create. Agentic AI is poised to alter the way in which companies function. However with larger autonomy comes larger accountability: knowledge safety and cybersecurity can not stay afterthoughts.
Organizations that embed governance, transparency, and resilience into their AI methods is not going to solely mitigate dangers but in addition construct the belief wanted to unlock AI’s full potential.